The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Cellular Communication
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) function as essential messengers in cellular communication, affecting diverse biological processes through their delivery of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Recent research underscores their potential in understanding cellular rejuvenation and implications in health. Through their interactions with target cells, EVs reveal critical information about cell health and functionality, making them a valuable focus in regenerative medicine.
Unveiling Mosquito EVs: A New Perspective
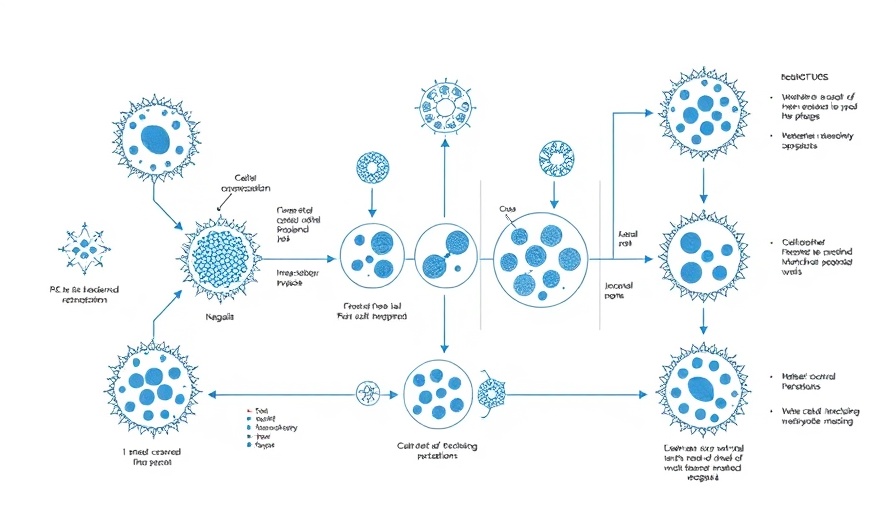
The recent study focusing on the characterization of EVs from the mosquito species Aedes aegypti sheds light on the size distribution and potential roles these vesicles might play in intercellular communication within insects. By employing advanced analytic techniques such as nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), researchers have unveiled that mosquito EVs have a majority size of less than 100 nm, fitting within the established ranges for exosomes found in mammalian models.
Advantages of Understanding EV Composition in Regenerative Medicine
In regenerative medicine, the importance of accurately characterizing the composition and function of EVs could lead to advancements in therapies focused on cellular health and rejuvenation. The identification of specific markers like the homolog of CD63 and the role of syntenin as potential markers for discrimination of EV types may enhance the therapeutic applications and efficacy of stem cell therapies, paving new pathways for senescence reversal and cellular repair.
The Connection Between Mosquito EVs and Human Cellular Health
While seemingly unrelated, the study of mosquito EVs and their biochemical properties may yield parallels to human health and disease processes. Understanding how these vesicles contribute to intercellular signaling can provide insights into mechanisms of cellular aging and the rejuvenation process, encouraging exploration into how EVs might support autophagy benefits and mitochondrial function.
Future Directions: Implications for Cellular Rejuvenation
The knowledge gained from the characterization of mosquito EVs holds promise not only for entomology but for holistic approaches to cellular health. As scientists continue to explore these cellular structures, the potential for developing NAD+ boosters and other interventions targeting EVs could revolutionize anti-aging strategies and overall vitality.
As we look towards the future, the growing body of research on EVs emphasizes the importance of multidimensional studies, integrating various aspects of cellular health and rejuvenation principles. With findings at the intersection of mosquito biology and cellular therapy, there lies a wealth of opportunity for breakthroughs in regenerative medicine and longevity.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment