Understanding the Rising Burden of Stroke in Older Adults
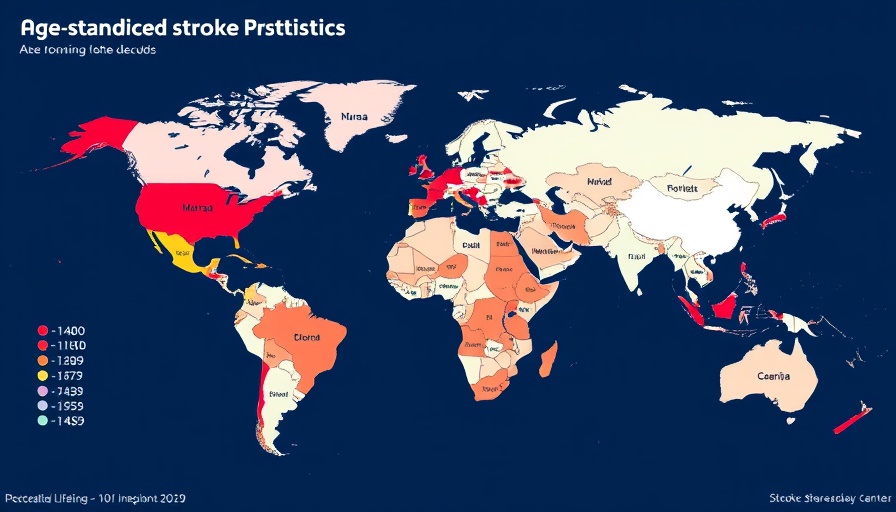
Stroke remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality globally, especially within the elderly population. A recent extensive analysis utilizing the 2021 Global Burden of Disease (GBD) dataset reveals a striking increase in the burden of stroke among older adults over the past three decades. Despite advancements in stroke management and rehabilitation, the data suggest that the overall number of stroke cases among the elderly has surged from approximately 4.39 million in 1990 to 8.19 million by 2021.
This rise in prevalence indicates a troubling trend despite a decline in age-standardized incidence rates, which fell from 996.06 to 775.68 cases per 100,000 people. This paradox highlights the complexity of stroke as both a growing public health issue and a condition that is becoming more manageable with modern medicine in some demographics.
Challenging Assumptions: Gender Differences in Stroke Burden
One of the surprising findings from the GBD study is the pronounced disparity in stroke burden between men and women in five Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) regions. It was reported that men consistently showed a higher burden when compared to women across various metrics. Given that stroke incidence rates equalize up until a certain age, researchers emphasize that the increasing burden on older men—especially post-55—serves as a critical warning signal that must shape prevention strategies.
How Lifestyle Choices Impact Stroke Risks in Aging Populations
The epidemiological evidence points to multiple modifiable risk factors contributing to stroke, such as smoking, air pollution, and physical inactivity. With the aging population more susceptible to these risks, adopting a proactive approach to wellness through lifestyle optimization is essential. Health-focused interventions, which may include dietary modifications and exercise regimens, could potentially decrease stroke incidence through better cardiovascular health and overall cellular rejuvenation.
The Role of Cellular Health in Stroke Prevention
As a growing body of research increasingly ties cellular health to overall well-being, telomere biology presents exciting insights into this area. Telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, play a crucial role in cellular aging processes. Telomere shortening is associated with various age-related diseases, including cardiovascular diseases like stroke. Through telomerase activation and supplements, researchers are exploring the potential for telomere maintenance as a strategy to improve health outcomes well into older adulthood.
Implications for Future Health Initiatives
Focusing on both prevention and education is paramount to combat the rising stroke burden in elderly populations. Innovative healthcare policies emphasizing regular screenings for at-risk individuals and educational campaigns promoting knowledge about stroke risk factors could prove beneficial. Additionally, integrating insights from telomere research and cellular regeneration into public health strategies may ultimately contribute to reducing stroke incidence and improving quality of life for millions.
Call to Action: Focus on Longevity and Stroke Prevention
As stroke remains a pressing global health challenge for older adults, it's imperative to prioritize preventive strategies rooted in scientific understanding. By embracing knowledge around factors like telomere health and lifestyle modifications, individuals can take actionable steps towards enhancing their longevity and reducing stroke risks. Consider discussing these aspects with healthcare professionals or exploring the burgeoning field of biohacking for personalized wellness strategies.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment