Exploring the Power of Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Combatting Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) represents a significant challenge in diabetes management, presenting a unique type of cardiac dysfunction linked to chronic hyperglycemia. Current therapies to address this condition are limited, prompting researchers to seek innovative solutions to restore cardiac function and improve overall health. Recent studies have revealed amniotic mesenchymal stem cells (AMSCs) as a promising treatment, particularly because of their capacity to inhibit detrimental processes such as pyroptosis through the modulation of specific signaling pathways.
The Role of the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway
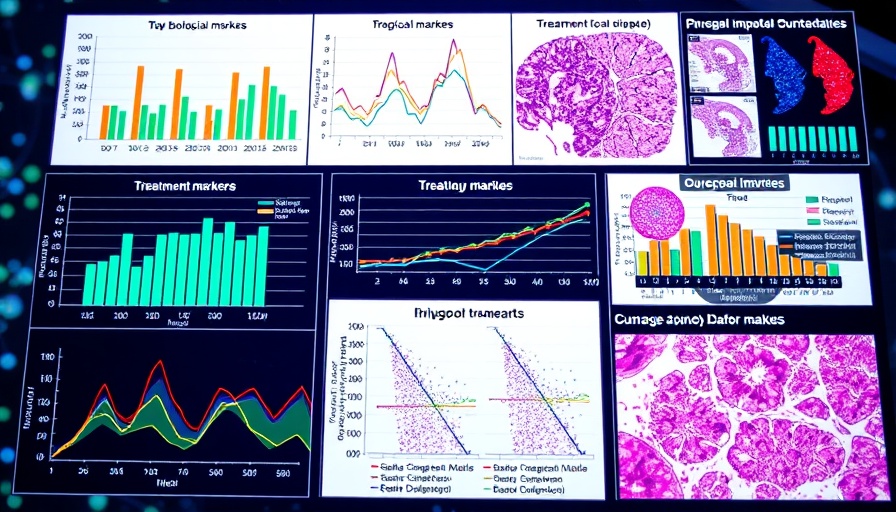
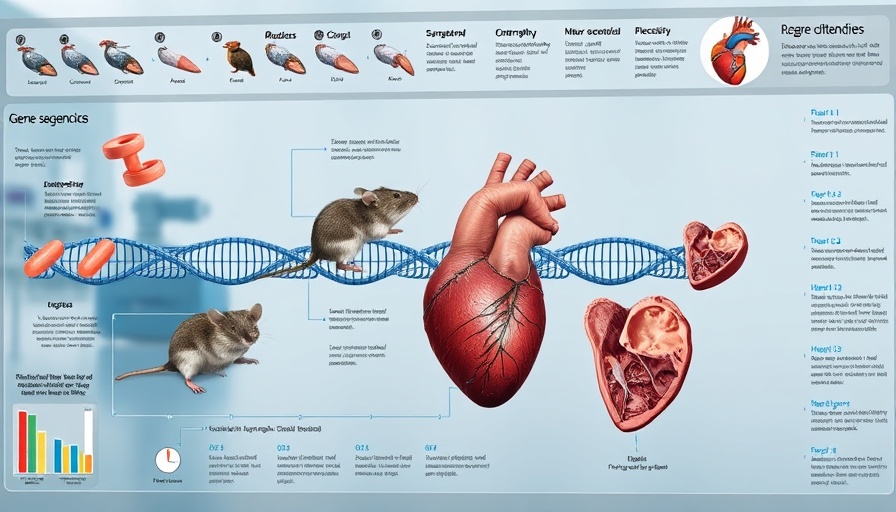
Understanding the underlying biological processes involved in DCM is crucial for developing effective interventions. The TLR4 signaling pathway, activated through MyD88 and NF-κB, plays a pivotal role in triggering inflammatory responses and pyroptosis—an inflammatory form of programmed cell death. The involvement of NLRP3 inflammasomes in this process exacerbates cardiac dysfunction by promoting inflammation and myocardial fibrosis, compounding the challenges faced by diabetic patients. AMSCs appeared to attenuate these negative effects by suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway, thereby reducing inflammation and improving cardiac morphology.
Impact of AMSCs on Cellular Health and Cardiac Function
In a comprehensive study, researchers employed a DCM mouse model, administering AMSCs through tail vein injections every two weeks. The results were promising: AMSCs significantly improved pancreatic function, reduced blood glucose levels, and enhanced insulin secretion. Moreover, cardiac function and structure experienced marked improvements. These findings suggest that AMSCs not only elicit favorable responses on blood glucose management but also play a vital role in cellular repair mechanisms, highlighting their potential in regenerative medicine.
Cellular Rejuvenation Through Stem Cell Therapy
The implications of AMSCs extend beyond merely treating diabetic conditions; their potential for cellular rejuvenation is noteworthy. These stem cells possess low immunogenicity and can differentiate into various cell types, supporting cellular health and potentially reversing aspects of cellular senescence. This characteristic can be particularly beneficial for health-conscious individuals seeking to maintain youthfulness and vitality into their later years. By mitigating risks associated with aging, AMSCs may offer a pathway to enhance mitochondrial function and overall cellular repair.
Future Perspectives on Stem Cell Applications
As research advances, the prospects of AMSCs in treating DCM and other degenerative conditions look increasingly promising. The modulation of inflammatory pathways exemplifies how targeted therapies can improve cardiac health in diabetic patients. The continued exploration of these therapies is essential, as they may ultimately reshape our understanding of regenerative medicine and its capacity to combat age-related health challenges.
Conclusion: The Path Towards Innovative Therapies
The findings surrounding amniotic mesenchymal stem cells offer new hope for effectively managing diabetic cardiomyopathy and enhancing cellular health overall. As the paradigm of treatment shifts from conventional methods to innovative solutions like stem cell therapy, it becomes imperative for health-conscious individuals to stay informed and consider incorporating scientific advancements into their health regimens. To learn more about how cellular rejuvenation strategies can benefit you, please explore the latest in regenerative medicine and its impacts on long-term health.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment